How ast-grep Works: A bird's-eye view
In the world of software development, efficiently searching, rewriting, linting, and analyzing code is essential for maintaining high-quality projects.
This is where ast-grep comes into play. Designed as a powerful structural search tool, ast-grep simplifies these tasks by leveraging the Abstract Syntax Tree (AST) representation of code. Let's break down how ast-grep works with the help of a diagram.
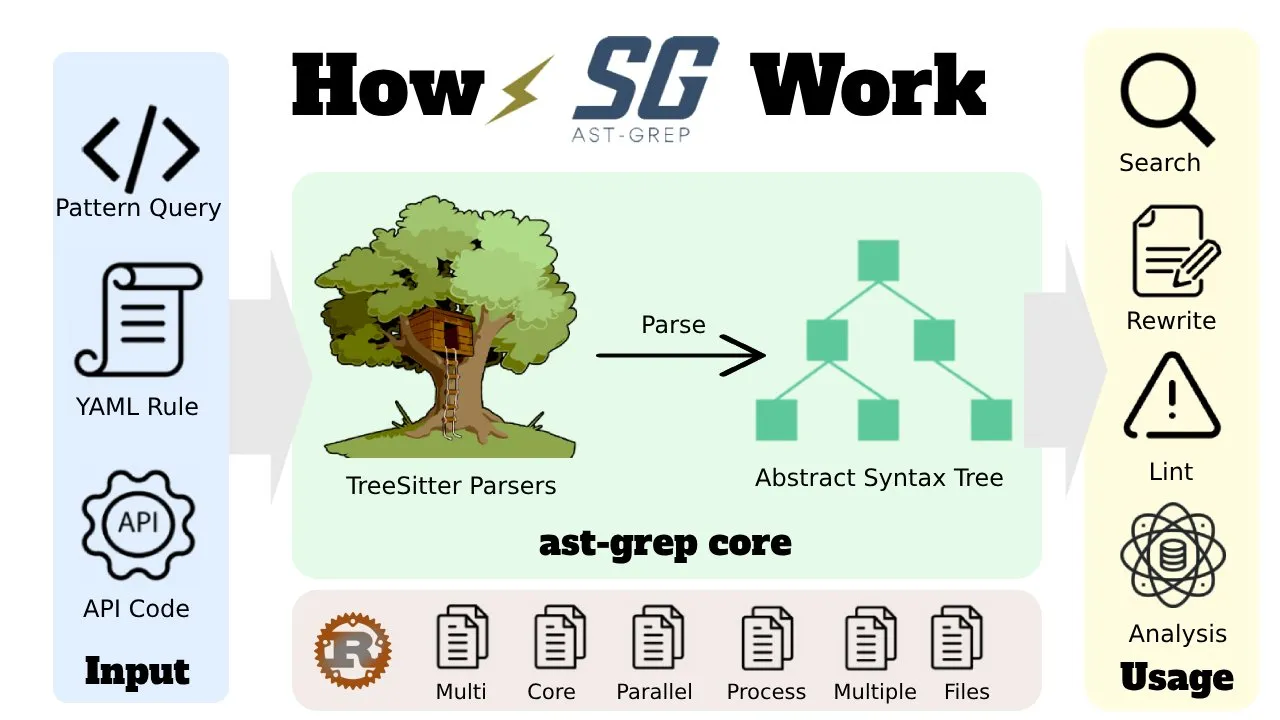
The Workflow of ast-grep
Generally speaking, ast-grep takes user queries of various input formats, parses the code into an AST using TreeSitter, and performs search, rewrite, lint, and analysis, utilizing the full power of CPU cores.
Query via Various Formats
ast-grep can accept queries in multiple formats, making it flexible and user-friendly. Here are some common query formats:
- Pattern Query: Users can define specific patterns to search for within their codebase.
- YAML Rule: Structured rules written in YAML format to guide the search and analysis process.
- API Code: Direct API calls for more programmatic control over the searching and rewriting tasks.
ast-grep's Core
ast-grep's core functionality is divided into two main components: parsing and matching.
1. Parsing with Tree-Sitter
The core of ast-grep's functionality relies on Tree-Sitter Parsers. TreeSitter is a powerful parsing library that converts source code into an Abstract Syntax Tree (AST). This tree structure represents the syntactic structure of the code, making it easier to analyze and manipulate.
2. Tree Matching
Once the code is parsed into an AST, the ast-grep core takes over and finds the matching AST nodes based on the input queries. Written in Rust, ast-grep ensures efficient performance by utilizing full CPU cores. This means it can handle large codebases and perform complex searches and transformations quickly.
Usage Scenarios
ast-grep can be helpful for these scenarios.
- Search: Find specific patterns or constructs within the code.
- Rewrite: Automatically refactor or transform code based on predefined rules or patterns.
- Lint: Identify and report potential issues or code smells.
- Analyze: Perform in-depth code analysis to gather insights and metrics.
Benefits of Using ast-grep
- Multi-Core Processing: ast-grep can handle multiple files in parallel by taking full advantage of multi-core processors. Typically ast-grep performs tasks faster than many other tools, making it suitable for large projects.
- Versatility: Whether you need to search for a specific code pattern, rewrite sections of code, lint for potential issues, or perform detailed analysis, ast-grep has you covered.
Example in the Real World
Pattern + Search: CodeRabbit uses ast-grep patterns to search code repo for code review knowledge. This example is collected from ast-grep's own dogfooding.
API + Rewrite: @vue-macros/cli is a CLI for rewriting at Vue Macros powered by ast-grep.
YAML + Lint: Vercel turbo is using ast-grep to lint their Rust code with custom rules.
Conclusion
ast-grep is a versatile and efficient tool for modern software development needs. By parsing code into an Abstract Syntax Tree and leveraging the power of Rust, it provides robust capabilities for searching, rewriting, linting, and analyzing code. With multiple input formats and the ability to utilize full CPU cores, ast-grep is designed to handle the demands of today's complex codebases.
Whether you are maintaining a small project or a large enterprise codebase, ast-grep can help streamline your development workflow.