Command Line Tooling Overview
Overview
ast-grep's tooling supports multiple stages of your development. Here is a list of the tools and their purpose:
- To run an ad-hoc query and apply rewrite:
ast-grep run. - Routinely check your codebase:
ast-grep scan. - Generate ast-grep's scaffolding files:
ast-grep new. - Develop new ast-grep rules and test them:
ast-grep test. - Start Language Server for editor integration:
ast-grep lsp.
We will walk through some important features that are common to these commands.
Interactive Mode
ast-grep by default will output the results of your query at once in your terminal which is useful to have a quick glance at the result. But sometimes you will need to scrutinize every result one by one to refine you pattern query or to avoid bad cases for edge-case code.
You can use the --interactive flag to open an interactive mode. This will allow you to select which results you want to apply the rewrite to. This mode is inspired by fast-mod.
Screenshot of interactive mode. 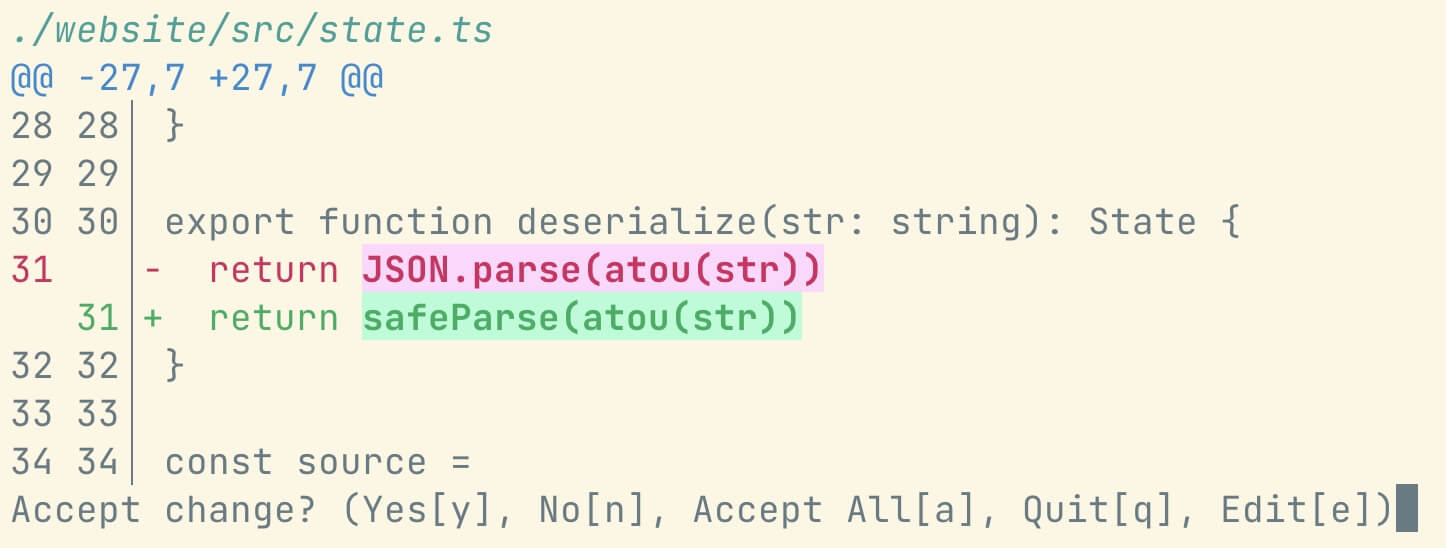
Pressing y will accept the rewrite, n will skip it, e will open the file in your editor, and q will quit the interactive mode.
Example:
ast-grep scan --interactiveJSON Mode
Composability is a key perk of command line tooling. ast-grep is no exception.
--json will output results in JSON format. This is useful to pipe the results to other tools. For example, you can use jq to extract information from the results and render it in jless.
ast-grep run -p 'Some($A)' -r 'None' --json | jq '.[].replacement' | jlessThe format of the JSON output is an array of match objects.
[
{
"text": "import",
"range": {
"byteOffset": {
"start": 66,
"end": 72
},
"start": {
"line": 3,
"column": 2
},
"end": {
"line": 3,
"column": 8
}
},
"file": "website/src/vite-env.d.ts",
"replacement": "require",
"language": "TypeScript"
}
]See JSON mode doc for more detailed explanation and examples.
Run One Single Query or One Single Rule
You can also use ast-grep to explore a proper pattern for your query. There are two ways to try your pattern or rule. For testing one pattern, you can use ast-grep run command.
ast-grep run -p 'YOUR_PATTERN' --debug-queryThe --debug-query option will output the tree-sitter ast of the query.
To test one single rule, you can use ast-grep scan -r.
ast-grep scan -r path/to/your/rule.ymlIt is useful to test one rule in isolation.
Parse Code from StdIn
ast-grep's run and scan commands also support searching and replacing code from standard input (StdIn). This mode is enabled by passing command line argument flag --stdin. You can use bash's pipe operator | to instruct ast-grep to read from StdIn.
Example: Simple Web Crawler
Let's see an example in action. Combining with curl, ast-grep and jq, we can build a simple web crawler on command line. The command below uses curl to fetch the HTML source of SciPy conference website, and then uses ast-grep to parse and extract relevant information as JSON from source, and finally uses jq to transform our matching results.
curl -s https://schedule2021.scipy.org/2022/conference/ |
ast-grep -p '<div $$$> $$$ <i>$AUTHORS</i> </div>' --lang html --json --stdin |
jq '
.[]
| .metaVariables
| .single.AUTHORS.text'The command above will produce a list of authors from the SciPy 2022 conference website.
JSON output of the author list
"Ben Blaiszik"
"Qiming Sun"
"Max Jones"
"Thomas J. Fan"
"Sebastian Bichelmaier"
"Cliff Kerr"
...With this feature, even if your preferred language does not have native bindings for ast-grep, you can still parse code from standard input (StdIn) to use ast-grep programmatically from the command line.
You can invoke ast-grep, the command-line interface binary, as a subprocess to search and replace code.
Caveats
StdIn mode has several restrictions, though:
- It conflicts with
--interactivemode, which reads user responses from StdIn. - For the
runcommand, you must specify the language of the StdIn code with--langor-lflag. For example:echo "print('Hello world')" | ast-grep run --lang python. This is because ast-grep cannot infer code language without file extension. - Similarly, you can only
scanStdIn code against one single rule, specified by--ruleor-rflag. The rule must match the language of the StdIn code. For example:echo "print('Hello world')" | ast-grep scan --rule "python-rule.yml"
Enable StdIn Mode
All the following conditions must be met to enable StdIn mode:
- The command line argument flag
--stdinis passed. - ast-grep is NOT running inside a tty. If you are using a terminal emulator, ast-grep will usually run in a tty if invoked directly from CLI.
The first condition is quite self explanatory. However, it should be noted that many cases are not tty, for example:
- ast-grep is invoked by other program as subprocess.
- ast-grep is running inside GitHub Action.
- ast-grep is used as the second program of a bash pipe
|.
So you have to use --stdin to avoid unintentional StdIn mode and unexpected error.
Running ast-grep in tty with --stdin
ast-grep will hang there if you run it in a tty terminal session with --stdin flag, until you type in some text and send EOF signal (usually Ctrl-D).
Bonus Example
Here is a bonus example to use fzf as interactive ast-grep launcher.
SG_PREFIX="ast-grep run --color=always -p "
INITIAL_QUERY="${*:-}"
: | fzf --ansi --disabled --query "$INITIAL_QUERY" \
--bind "start:reload:$SG_PREFIX {q}" \
--bind "change:reload:sleep 0.1; $SG_PREFIX {q} || true" \
--delimiter : \
--preview 'bat --color=always {1} --highlight-line {2}' \
--preview-window 'up,60%,border-bottom,+{2}+3/3,~3' \
--bind 'enter:become(vim {1} +{2})'Editor Integration
See the editor integration doc page.
Shell Completions
ast-grep comes with shell autocompletion scripts. You can generate a shell script and eval it when your shell starts up. The script will enable you to smoothly complete ast-grep command's options by tabbing.
This command will instruct ast-grep to generate shell completion script:
ast-grep completions <SHELL><SHELL> is an optional argument and can be one of the bash, elvish, fish, powershell and zsh. If shell is not specified, ast-grep will infer the correct shell from environment variable like $SHELL.
The exact steps required to enable autocompletion will vary by shell. For instructions, see the Poetry or ripgrep documentation.
Example
If you are using zsh, add this line to your ~/.zshrc.
eval "$(ast-grep completions)"Use ast-grep in GitHub Action
If you want to automate ast-grep linting in your repository, you can use GitHub Action, a feature that lets you create custom workflows for different events.
For example, you can run ast-grep linting every time you push a new commit to your main branch.
To use ast-grep in GitHub Action, you need to set up a project first. You can do this by running ast-grep new in your terminal, which will guide you through the process of creating a configuration file and a rules file.
Next, you need to create a workflow file for GitHub Action. This is a YAML file that defines the steps and actions that will be executed when a certain event occurs. You can create a workflow file named ast-grep.yml under the .github/workflows/ folder in your repository, with the following content:
on: [push]
jobs:
sg-lint:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
name: Run ast-grep lint
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: ast-grep lint step
uses: ast-grep/action@v1.4This workflow file tells GitHub Action to run ast-grep linting on every push event, using the latest Ubuntu image and the official ast-grep action. The action will check out your code and run ast-grep scan on it, reporting any errors or warnings.
That's it! You have successfully set up ast-grep linting in GitHub Action. Now, every time you push a new commit to your main branch, GitHub Action will automatically run ast-grep linting and show you the results. You can see an example of how it looks like below.
For more information, you can refer to the ast-grep/action repository, where you can find more details and options for using ast-grep in GitHub Action.
Colorful Output
The output of ast-grep is exuberant and beautiful! But it is not always desired for colorful output. You can use --color never to disable ANSI color in the command line output.